Risk Management Risk Management for Business Process Improvement: The Foundation of Effective ERM
Risk management process improvement is the identification of your organization’s business processes, followed by process-owners accountability for, compliance, performance goals, and risk vulnerabilities.
All operational activities at your organization occur inside of defined business processes.Therefore, so too do all risks, mitigation activities, and monitoring processes. Risk management process improvement allows you to more consistently identify those risks and design appropriate controls, without impeding growth or innovation. LogicManager recognizes that end-to-end processes consist of multiple levels of sub-processes. The level of granularity, meaning the extent to which processes are broken down into smaller processes, evolves over time. Our tool is built to support this evolutionary process. You might choose to get granular in areas of greater priority and fill out the others over time.
The process defined above — applying risk management to process improvement — is a means of operationalizing, or implementing, policies. It is one thing to identify a risk and design a process for mitigating that risk. It is another to ensure the mitigation process is actually executed. To do so, you need transparency throughout the organization, a way for departments to communicate (i.e. bridge silos), and a way to assign the accountability discussed above. Risk management process improvement is the way to achieve these three components.
The LogicManager Platform Provides:
An ERM plan is the basic communication platform used throughout LogicManager to gather, organize and report information. It serves as an organizer for all information and files entered and saved within LogicManager for a particular business process, department, facility, or project. Each plan can have any number of plan owners, or a group/committee of owners, who are responsible for coordinating the ERM Plan.
ERM plans include activities for assessing risk vulnerabilities, readiness compliance standards, performance goals and associated financial elements, standard operating procedures, controls, notes, tasks, and documents.
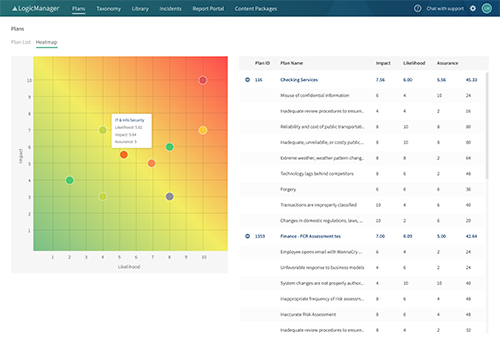
Business process risk management must be contextualized by the nature of what activity is being done. Context includes the level where risks, compliance or goal achievement could develop and materialize. The more granular the assessment, the more accurate and useful the result, and the more mature the ERM competency. Context is typically set around a sub-process, project, customer, vendor, or other element of the business and then combined and aggregated to an enterprise level.