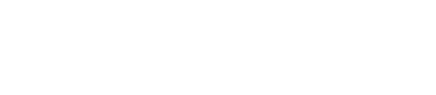What is Third Party Risk Management?
Last Updated: May 23, 2025
Third-party risk management (TPRM) becomes more vital as businesses increase their reliance on external service providers. Each third-party vendor you work with has unique processes, policies, security strategies and regulations it must follow, which can enhance or harm your business depending on their effectiveness.

Implementing advanced third-party risk management solutions in your company can help you identify risks early. TPRM platforms are more than simple vendor management systems — they expand on the basic safeguards to explore the broader implications of third-party relationships and identify risks that would otherwise go undetected.
As third-party relationships evolve with advancing digital business environments, assessing your vendors and ensuring their security efforts align with your needs is more important than ever. This guide outlines a comprehensive TPRM approach to improve business protection, compliance, efficiency and performance.
Table of Contents
- What Is TPRM?
- The Evolution and Importance of TPRM in Today’s Business Environment
- Types of Third Parties and Their Unique Risk Profiles
- Critical Risk Domains in Third-Party Risk Management
- The Complete Third-Party Risk Management Life Cycle
- Third-Party Due Diligence: Comprehensive Strategies and Methodologies
- How to Build an Effective Third-Party Risk Management Framework
- Navigating the Complex Regulatory Landscape of Third-Party Risk Management
- Leveraging Technology to Transform Your TPRM Program
- Advanced Third-Party Risk Management Strategies for Mature Programs
- How LogicManager Transforms Third-Party Risk Management
- Measuring the Success of Your Third-Party Risk Management Program
- Discover the Future of Third-Party Risk Management With LogicManager’s AI-Powered Solutions
What Is TPRM?
TPRM is the proactive process of assessing and monitoring your potential risks when working with external vendors. Third-party vendors, offering services such as accounting, shipping, logistics, maintenance, supply and IT support, are commonplace in business today.
Even if your business follows strict security guidelines, TPRM is a vital part of protecting your information throughout the sales cycle because your third-party vendors may lack the same level of security. If third-party vendors fail to protect their own systems effectively, they can unintentionally breach contracts or allow cybercriminals to access your information.
The Evolution and Importance of TPRM in Today’s Business Environment
Modern TPRM advancements enhance protection against sophisticated cybersecurity threats, helping businesses safeguard sensitive information.
Elevated Risk Profiles and the Need for Enhanced TPRM
In today’s business world, there is an increased reliance on third-party vendors. Working with third-party vendors is essential but presents more risks than it used to, as businesses shift to using software as a service (SaaS) and cloud-based solutions. This adds more external vendors to the process and opens up additional vulnerabilities for cybercriminals to target your systems and data.
The more vendors you work with, the more alert you must be to potential vulnerabilities within their processes and systems. Any weak area in their safeguards opens your business up to a potential cyberattack. Advanced TPRM is crucial for combating these attacks from all angles.
The Shift From Compliance-Focused Strategies to Risk-Based Approaches
Traditionally, TPRM was a compliance-based approach that primarily focused on meeting regulations. While compliance is vital, focusing solely on meeting regulations ignores the importance of proactively managing risks.
The shift to a risk-based approach has significantly enhanced TPRM because it can effectively combat advanced threats. Risk-based strategies combine compliance with continuous monitoring, focusing more on evolving threats. This enables companies to address potential risks before a data breach or cyberattack occurs.
Current Trends Shaping TPRM in 2025 and Beyond
Explore some of the current trends shaping TPRM:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) integration: AI is an incredible tool that’s transforming various aspects of cybersecurity. Cybercriminals can use AI to enhance their tactics, and cybersecurity professionals must use it to mitigate these advanced threats. AI can rapidly process vast amounts of data and recognize patterns, offering deeper insights and making TPRM more effective.
- Automation: The increase in AI-powered TPRM methods also increases automation. AI technology makes it possible to automatically identify, monitor and assess risks with less manual intervention.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology records transactions with transparency, protecting sensitive data from theft. This supports TPRM efforts by providing a secure ledger for third-party data and transactions, and it increases trust in stakeholders and consumers.
Types of Third Parties and Their Unique Risk Profiles
Understanding the potential risks from different types of third-party providers is important for identifying the specific safeguards your company should focus on. Each party can directly affect your company’s cybersecurity posture and vulnerabilities.
Consider how the following types of vendor risks can impact your systems and operations.
Vendors and Suppliers
Your vendors and suppliers likely handle a significant amount of personal and financial information, which puts your company and customers at higher risk.
Supply chain attacks, compliance mistakes or data breaches can potentially leak your company’s or your customers’ sensitive information to cybercriminals.
For example, you might use your company’s bank account or a business card to pay for raw materials. If your material supplier falls victim to a data breach, cybercriminals could potentially steal your company’s financial information and use it for their personal gain.
Contractors, Consultants and Service Providers
Contractors, consultants and service providers are the professionals you depend on for managing critical functions such as the following:
- IT support
- Legal counsel
- Marketing guidance
- Banks
- Accountants
- Payment processing systems
- Data management
- Financial advisors
- Investment firms
- Marketing agencies
If any of your service providers mishandle data, implement ineffective security practices or experience a service disruption, cybercriminals could gain access to your company’s sensitive systems and information.
Channel Partners and Distributors
Channel partners are the third-party companies you collaborate with to promote, sell or distribute your products or services.
When collaborating with another company to expand your reach, ensuring you are on the same page with them regarding important cybersecurity practices is critical.
Channel partners and distributors can introduce a wide variety of cybersecurity risks because they also work with their own third-party vendors. This network of partners can introduce new vulnerabilities, especially if any of the organizations neglect valuable security protocols.
Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
If you share ownership and control with another company through a joint venture or strategic alliance, enhancing your TPRM is vital. Collaborations often involve different security systems, various levels of risk awareness and a larger surface area for potential attacks.
Cloud Providers and Data Processors
Cloud providers and data processors host critical applications and manage significant amounts of sensitive data.
The following are third-party risks associated with cloud providers and data processors that can significantly impact your company’s data:
- Service outages
- Data breaches
- Noncompliance with privacy regulations
- Noncompliance with data sovereignty
Critical Risk Domains in Third-Party Risk Management
Consider how the following risk domains can directly or indirectly impact your organization.
Information Security and Cyber Risks
Protecting sensitive information is one of the most vital parts of TPRM. Unauthorized individuals gaining access to your company’s information can result in data theft, productivity disruptions, financial losses and reputational damage.
To protect sensitive information and block unauthorized access for both your organization and its vendors, prioritize the following:
- A robust cybersecurity posture
- Advanced breach notification systems
- Comprehensive data protection measures
Data Privacy and Protection
Data privacy and protection are closely intertwined with information security. You must ensure your organization and third-party providers safeguard the personal data of all customers and involved parties. This means ensuring compliance with data privacy laws and regulations. It also entails practicing ethical data usage and storage procedures.
Business Continuity and Operational Resilience
Operational risks develop when a third-party service provider’s operations come to a halt. This can occur for any of the following reasons:
- IT or power outages
- Natural disasters
- Fires
- Process or system failures
- Control failures
- Human error
These disruptions can threaten your business continuity by interrupting important daily activities.
For example, an IT outage in your cloud provider’s systems can cause your organization to lose computing power, security, data access or application usage. Without these essential elements, your company may be unable to deliver the products and services your customers expect, putting your reputation at risk.
Establishing a plan for how your team will remain operational in the event a vendor experiences disruptions is crucial for protecting your bottom line.
Financial Stability and Viability
A third-party service provider’s economic health can impact your company’s financial security.
If a provider faces financial challenges, they may lose resources to deliver quality services. This often leads to slow response times, system outages, contract breaches or unreliable outcomes.
If this occurs, you may experience business delays and lose sales or customers. You might also incur additional costs if you face fines and legal fees or need to find alternative vendors in a pinch.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks
These risks occur when your organization’s third-party service providers fail to comply with relevant industry guidelines or laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS).
If providers fail to comply with the regulations they are required to follow, they can face legal actions or fines that ultimately impact your business operations.
Your organization may also face hurdles if a third-party service provider fails to comply with the regulations you are required to follow or with your company’s internal policies.
ESG and Reputational Risks
Cybersecurity is more than a technological issue. More companies are focusing on environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors in their TPRM. These risks can lead to potential environmental, legal and business reputation risks as well as harm to vulnerable populations.
Learn more about ESG risks through the following TPRM examples:
- Environmental: Environmentally friendly technologies, such as renewable energy systems and smart grids, require protection from cyberattacks that could interrupt operations.
- Social: Protecting data and private information is your organization’s social responsibility. An accidental data leak could put your consumers at risk of having their information stolen, which can damage your reputation and cause your target market to lose trust in you.
- Governance: It’s important that your company operates with integrity, accountability and transparency. An effective TPRM strategy can help you ensure ethical conduct in your processes.
Geopolitical and Geographic Risks
Geopolitical and geographic risks can stem from the following domestic and international occurrences:
- Political decisions
- Major events
- Trade policies
- International and domestic conflicts
- Sanctions
- Political unrest
Without effective safeguards in place, these risks can disrupt operations, lead to financial instability and threaten your business continuity. Consider how geopolitical and geographic occurrences could potentially impact your company, and plan your response accordingly.
Fourth-Party or Nth Party Risks
Fourth-party, also known as Nth-party, risks are those that occur deeper in the supply chain.
These risks are associated with the service providers, partners and subcontractors that your vendors depend on — and, potentially, the extended network of their providers that those partners also work with.
While you don’t directly work with these fourth-party organizations, they can indirectly impact your company. Modern businesses like yours operate within complex, multi-tier supply chains beyond your immediate vendors, so considering security and risk management levels at all levels is essential.
The Complete Third-Party Risk Management Life Cycle
The TPRM process involves the following stages:
1. Initial Assessments and Risk-Based Third-Party Categorization
Initial TPRM assessments provide a comprehensive view of each vendor’s workflow, processes and security. Pay close attention to the tools, safeguards and policies they use to handle your information, and classify all of your vendors into different risk levels based on their potential impact on your company.
2. Pre-Contract Due Diligence
Pre-contract due diligence is one of the most important stages in the TPRM process. Ensure you evaluate each vendor’s security measures, operations, compliance and policies before signing any contracts or service-level agreements (SLAs) with them.
Ensure each legal agreement includes actions a vendor will take if you find them to be in breach of a contract or compliance regulations.
3. Contract Negotiation and Risk Transfer
A well-crafted contract shields you from unforeseen complications and risks. Each contract you sign should include provisions that address factors such as:
- Regulatory compliance.
- Breach notification protocols.
- Cybersecurity measures.
- A right to audit.
4. Onboarding With Appropriate Controls
When onboarding a third-party service provider, ensure all of the vendor’s personnel who handle your information understand the correct protocols.
Provide necessary details about your TPRM policies, security standards and reporting protocols before integrating a vendor into your systems so they clearly understand how to safeguard your data.
5. Ongoing Monitoring and Periodic Reassessment
Ongoing monitoring is essential for effective risk management. It enables your team to detect potential issues early on and take action to protect your organization. Continuously assess your third-party vendors to ensure they remain compliant with your policies and TPRM regulations.
6. Offboarding and Termination Management
Your offboarding process should include the following steps to protect your company from data breaches, financial losses and intellectual property theft when you terminate a relationship with a vendor:
- System access removal
- Data disposal
- Final audits
Third-Party Due Diligence: Comprehensive Strategies and Methodologies
Due diligence is one of the most important parts of third-party risk management. The following comprehensive strategies and methodologies can help you practice due diligence in your TPRM approach.
Questionnaires and Assessments
Third-party risk assessments and questionnaires help you collect information about each vendor’s security practices, operations, risk management systems and compliance. Tailor your questionnaires to the specific types of vendors you work with, and use a scoring system to evaluate their responses.
You can use these tools to detect potential risks early in your relationships with third-party service providers and make informed decisions about how you work with them moving forward.
Document Collection and Review Processes
Documentation is a vital part of compliance and business security. Create a checklist of all required documents, and establish a secure document submission process for retrieval and review.
Proper documentation and recordkeeping enable your company to closely evaluate each vendor’s policies, identifying compliance and security gaps so you can effectively address them.
On-Site Assessments and Virtual Audits
Visit vendor sites to evaluate their operations, controls, compliance and security measures in person.
If you work with remote vendors, you can use collaboration tools and video conferencing to conduct virtual TPRM audits. An on-site or virtual audit is an excellent opportunity to catch potential risks you might miss through questionnaires or document reviews alone.
On-site and virtual audits facilitate real-time discussions and observations, providing you with a deeper understanding of each vendor’s operations and risk management practices.
Technical Testing and Vulnerability Scanning
Validating a vendor’s technical safeguards is vital to ensure their IT systems are secure. Establish protocols for assessing each vendor’s IT system through penetration testing, vulnerability scans and security assessments. This helps you evaluate if vendors implement effective security measures to protect sensitive systems and information.
Hiring third-party security experts to perform technical assessments and analyze the results is the best way to ensure accuracy.
Financial Analysis and Viability Assessments
Collecting and analyzing vendors’ financial documents, such as credit reports and financial statements, helps you assess the following factors:
- Stability
- Financial health
- Ability to meet compliance and contractual obligations
Financial analysis and viability assessments are important for identifying vendors who may be at a higher risk of financial instability.
Reputation and Adverse Media Screening
A vendor’s negative media coverage can adversely impact your company, so you should closely screen each third-party service provider’s reputation to evaluate their public perception. Use the following tools to assess your providers’ reputations:
- Local and national news outlets
- Social media platforms
- Online reviews
- Customer testimonials
- Discussion boards
- Industry forums
- Professional networks such as LinkedIn
- Regulatory agency reports
How to Build an Effective Third-Party Risk Management Framework
The following stages can help your organization establish a successful third-party risk framework.
Program Governance Structure
To establish a program governance structure, you must define your TPRM program’s management and oversight framework.
Align your TPRM objectives with your organization’s overall risk management strategy, and ensure accountability by identifying the following key stakeholders:
- Risk committees
- Senior management
- Compliance teams
Policy and Standard Development
Standards and policies are vital for maintaining a consistent TPRM approach. Develop a formal TPRM policy outlining your company’s main objectives and assessment procedures for managing third-party risks. In doing so, you can identify the full scope of your potential risks and how you plan to address them.
Establishing standards for the following is also crucial to ensuring you effectively and consistently evaluate third-party relationships:
- Risk classifications
- Vendor assessments
- Monitoring practices
Role and Responsibility Definitions
Clearly-defined roles and responsibilities ensure your company successfully implements its TPRM strategy. Specify which individual in your company is responsible for each task, and precisely define their responsibilities within that role.
Roles may involve tasks such as completing vendor assessments, reporting potential risks or monitoring third-party relationships.
When you clearly define responsibilities, you can ensure each team member understands the importance of their role and how they contribute to the company’s overall TPRM approach.
Maturity Model Progression
Maturity model progression frameworks help companies evaluate existing TPRM capabilities, identify weaknesses and determine how to improve. Use a maturity model progression to outline the stages your company moves through as you develop capabilities in your risk management approach.
Your company transitions into each stage as your team reaches a higher maturity level, indicating greater effectiveness, reliability and efficiency within that level. This enables you to create a strategy for gradually improving your TPRM approach and ensuring it evolves to combat changing regulations and risks.
The following progression is a common framework for TPRM applications:
- Initial or ad-hoc stage: During the initial stage, your TPRM activities are unstructured. You haven’t yet standardized your processes or established a formalized program. This is when you first start to lay the groundwork for your risk management strategy.
- Developing or fragmented: As you transition into the developing stage, your organization has an established TPRM program in a basic form. At this point, you may have the framework of a TPRM program without a dedicated team, standardized processes or clear guidelines.
- Defined or managed: Your company reaches the defined or managed stage when you formally establish clear procedures, roles, responsibilities and policies. At this level, you have a dedicated team in place and have started to monitor your TPRM program actively.
- Integrated or scalable: In the integrated or scalable stage, you have fully integrated your TPRM program into your organization’s risk management framework. This is when you start to focus on making data-driven decisions and continuously improving your processes.
- Agile or optimizing: By the agile or optimizing stage, you have a proactive, adaptive TPRM program and a strong focus on continuous improvement. During this stage, your team proactively manages risks by leveraging predictive risk assessments and advanced analytics.
Reporting Structures and Metrics
Reporting structures and metrics are vital for tracking your TPRM program’s effectiveness. Clearly define the following key performance indicators (KPIs) to track your strategy’s success, identify areas for improvement and maintain communication with stakeholders:
- The number of vendor assessments you complete
- Identified risk levels
- Reported incidents
Resource Allocation and Budgeting
Allocating your resources effectively is crucial for TPRM program sustainability. First, you must identify necessary resources, such as the following, to implement a successful program:
- Personnel
- Training
- Technology such as software and analytic tools
Identify the precise resources you need to continuously assess and monitor potential risks and meet regulations. When you effectively manage your budget, you can easily adapt to changing risks.
Navigating the Complex Regulatory Landscape of Third-Party Risk Management
Your organization must follow general and specific regulations based on your industry. Consider which of the following standards you and your third-party service providers must adhere to.
Financial Services Regulations
Any organization or service provider that offers financial guidance or handles money must adhere to the following types of regulations:
- OCC: The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) supervises and regulates federal savings associations and national banks. OCC guidelines ensure that financial institutions comply with laws to protect consumers and maintain safe federal banking.
- FDIC: The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a government agency that protects depositors and consumers from bank failures.
- FRB: The Federal Reserve Board (FRB) regulates banks and bank holding companies. It enforces guidelines to protect consumers and ensure banking system stability.
Healthcare Regulations
Any company that provides healthcare services must comply with the following regulations:
- HIPAA: Following HIPAA regulations protects sensitive information, such as personal health information and medical records. Healthcare organizations and their third-party service providers must meet regulations to maintain patient information confidentiality.
- HITECH: The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) strengthens HIPAA enforcement and ensures electronic health records (EHRs) are used responsibly. It also expands on HIPAA regulations to include the business associates of covered entities.
Privacy Regulations
You and your third-party vendors may be required to meet some of these privacy regulations:
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation is a law specific to the European Union that regulates how organizations handle the personal data of citizens in the European Union (EU). Any organization that collects, manages or processes data from individuals in the EU must adhere to GDPR guidelines.
- CCPA and CPRA: The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) are privacy laws specific to California that regulate how organizations can collect, use and share the personal information of California residents.
- PIPEDA: The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) regulates how organizations manage the personal information of Canadian citizens.
Industry Standards
Depending on your specific products or services, you may also need to comply with industry standards such as the following:
- ISO 27001: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001 requires organizations to address supply chain risks by implementing and maintaining a strong information security management system (ISMS).
- NIST: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) enforces guidelines and standards to improve federal information systems’ cybersecurity. If your company is part of the private sector, provides services for the private sector or works with the private sector in any form, you must ensure you follow NIST standards.
- SOC 2: The System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC2) reporting framework evaluates controls for service providers that manage customer data. The American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) uses SOC2 to assess controls related to data security, confidentiality, privacy, availability and processing integrity, ensuring organizations implement effective risk management practices and achieve operational effectiveness.
Leveraging Technology to Transform Your TPRM Program
Technology advances rapidly, presenting new risks as well as enhanced tools to combat them.
Upgrading your risk management approach to keep up with evolving threats is a necessity, and advanced solutions can help. The following technology can significantly enhance your TPRM program.
Integrated ERM Platforms
An integrated enterprise risk management (ERM) platform provides a comprehensive view of your organization’s risks across your entire risk landscape. It combines risk data from multiple sources to help you make informed decisions in all areas of your third-party vendor relationships.
TPRM-Specific Solutions
TPRM-specific solutions, such as vendor risk management (VRM) software, are some of the most effective ways to combat third-party risks.
VRM focuses on the potential vulnerabilities of external entities to make the following easier:
- Assessing each third-party service provider’s security practices
- Monitoring vendor performance
- Identifying and mitigating potential risks early
Continuous Monitoring Tools
Continuous monitoring tools track your IT systems’ and third-party vendors’ security, compliance and performance in real time. Automated systems can help you detect vulnerabilities early and proactively mitigate risks before they cause significant damage.
Security Rating Services
A security rating service measures the security posture of organizations and their third-party service providers.
Security rating services are invaluable resources because they can help organizations streamline their third-party vendor assessments and enhance remediation efforts.
AI and Automation Capabilities
As mentioned earlier, AI and automation capabilities can help your organization do the following:
- Accelerate processes
- Boost efficiency
- Gain greater insights into potential risks
Integrating AI and automation technology in your TPRM program is one of the best ways to keep up with evolving threats.
Integration With Procurement and Contract Systems
Integrating your TPRM program with your procurement and contract systems is an excellent way to streamline your processes. This can also help your organization gain a more comprehensive perspective.
Integration centralizes your data so you can view all of your vendor information, security assessments, compliance documents and contract terms in one place.
Advanced Third-Party Risk Management Strategies for Mature Programs
The following forward-looking approaches can help your organization maintain a mature TPRM program:
- Collaborative third-party assessments: Collaborative assessments allow your business to involve multiple stakeholders in your evaluations and decision-making processes. Improving communication and sharing responsibilities leads to more diverse expertise, deeper understandings and comprehensive assessments.
- Fourth-party and supply chain mapping: Fourth-party and supply chain mapping help you identify potential risks associated with the vendors that your third-party service providers work with.
- Concentration risk management: Concentration risk management can help you identify where to diversify your company’s service providers for critical services. Diversifying your vendor base helps minimize the impact in the event you experience a supply chain failure or disruption.
- Resilience testing and scenario planning: Resilience testing and scenario planning help you evaluate how well your organization and its service providers can recover from disruptions, cyberattacks or breaches. Plan disruption simulations to help your organization identify areas for improvement.
- Real-time risk intelligence: Real-time risk intelligence involves leveraging technology and analytics to deliver immediate insights or alerts. With this strategy, you can identify industry trends, regulatory changes and emerging risks in their earliest stages to respond to threats as early as possible.
How LogicManager Transforms Third-Party Risk Management
LogicManager takes a TPRM-specific risk taxonomy approach to protecting your company’s data, systems and reputation. Our third-party risk management software includes pre-built assessment templates and risk libraries, and it integrates seamlessly with your procurement and contracting systems.
With automated workflow and monitoring capabilities, your team has more time to focus on growing the business and greater peace of mind knowing your company is protected.
Strengthen Compliance and Protect Your Reputation With LogicManager
LogicManager offers risk management software, advanced analytic tools and TPRM templates to help you stay ahead of evolving threats.
Risk Ripple Analytics, an AI-powered collection of tools, exposes interconnected risks that would normally go undetected. With LogicManager’s holistic third-party risk management software, you can do the following to strengthen your compliance:
- Use taxonomy technology to map your third-party assessments and controls to external regulations and internal policies
- Identify significant third parties and associated threats with intuitive risk assessments
- Automatically pull crucial points and terminology from contracts using AI technology, ensuring your company is aware of all details
- Use comprehensive contract insights to make informed decisions
- Automatically initiate contract reviews to meet key deadlines
- Closely collaborate with your third-party vendors and gather crucial information on one customizable interface
- Receive recurring reminders, alerts and time-sensitive task notifications for crucial elements such as contract renewals and review dates
Measuring the Success of Your Third-Party Risk Management Program
The following KPIs and metrics can help you maintain a successful TPRM program:
- Risk reduction measurements to gauge successful risk mitigation or identify areas for improvement
- Efficiency metrics, such as the average time your company spends on risk assessments
- Coverage and completeness indicators to assess how thorough your evaluations are
- Compliance achievement metrics to monitor your vendors’ adherence to your internal policies and external security regulations
- Financial impact and calculated cost savings of incident reductions
Discover the Future of Third-Party Risk Management With LogicManager’s AI-Powered Solutions
Protect your company’s data, reputation and processes with the right third-party risk management guidance. LogicManager offers advanced risk management software and analytic tools to help your company anticipate what’s ahead, protect your reputation and enhance performance.
Our scalable solution packages can help you cover every area of your business, including vendor management and IT governance. We provide AI-powered ERM software that guides you through a risk-based process of effective threat identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring and reporting. With LogicManager’s TPRM solutions, you can take a proactive, efficient approach to protecting your company.
Request a demo to discover how you can improve your TPRM strategy and mitigate risks before they develop.